Neat Tips About How To Treat A Poisonous Snake Bite
Avoid contact with snakes.
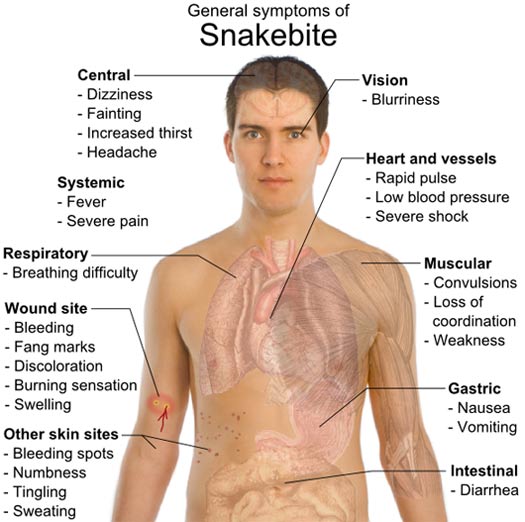
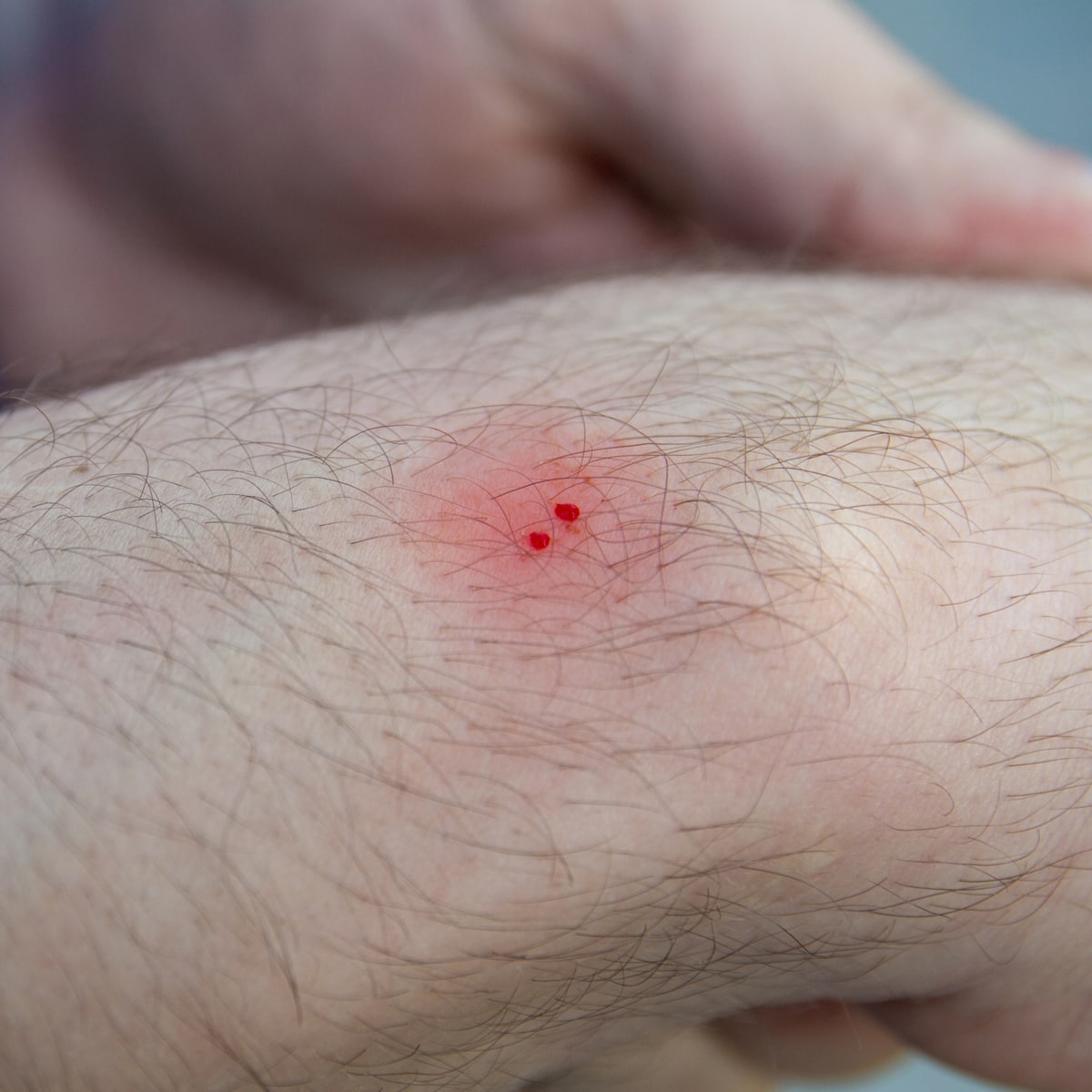
How to treat a poisonous snake bite. Wash the bite with soap and water. Cover the bite with a bandage. However, it’s essential to get to a medical facility.
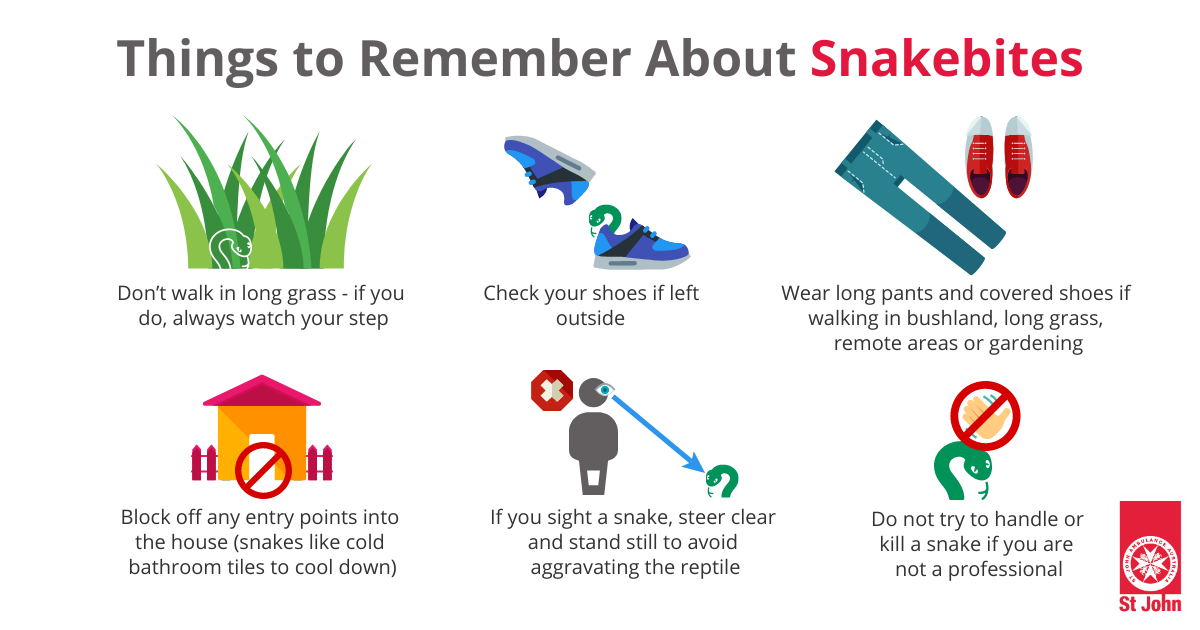
A snakebite is an injury that happens when you’re bitten by a snake. Types of uk snake only 3 types of snake are found in the wild in the uk. According to wilderness experts, here are the best ways to avoid snakes and their bites:
You may have heard some tips for snake bite care that can be harmful. Cover the bite with a clean, dry dressing. First aid steps you can take after a snake bite occurs include cleaning the wound, remaining calm, and immobilizing the affected area.
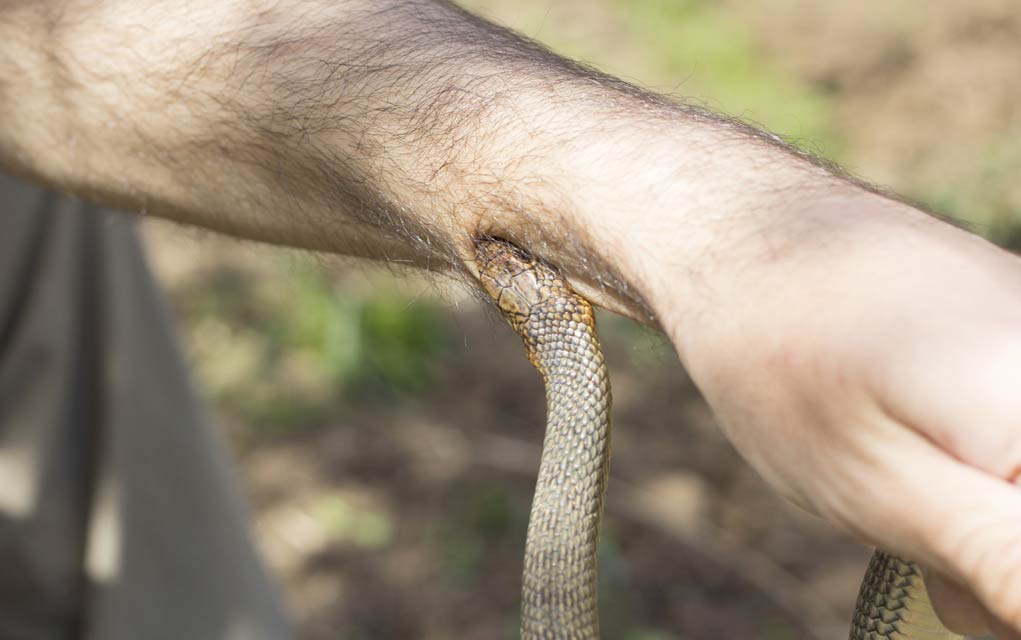
Do not do any of the following: Wash the wound with warm soapy water immediately. In the united states can inject poison when they bite.
All venomous snake bites can be effectively treated with antivenom. In north america, these include the rattlesnake, coral snake, water moccasin, also called cottonmouth,. Of snakes worldwide and 20%
Never handle a venomous snake, not even a dead one or its decapitated head. Call triple zero (000) and ask for an ambulance. Lay or sit the person down with the bite below the level of the heart.
Don’t sleep or rest next to areas where snakes may be hiding. 1 determine the type of bite. Dermatology emergency medicine first aid how we reviewed this article:
Cut a bite wound; The most common venomous snakebites are caused by the following snakes: Worldwide, there are about 20,000 to 100,000 snakebite deaths per year.
Do not pick up the snake or try to trap it. Cover with a clean, dry bandage. There are antivenoms that treat bites from a specific type of snake (monospecific antivenoms) and also those that treat bites from a number of snakes found in a particular geographic region (polyspecific antivenoms).
Tell them to stay calm and still. Researchers have discovered a potent antibody that can neutralize a key type of neurotoxin produced by four different deadly snake species from south asia, southeast asia, and africa—a step toward an antivenom that could be used on any of the 200 or so dangerous venomous snakes throughout the world. Mark the edge of the bite to track any changes or growth in redness or swelling.